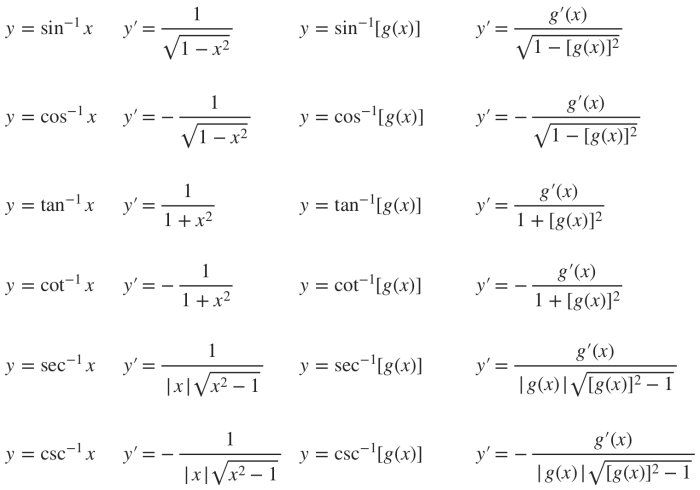Derivatives of inverse trig functions worksheet – Embark on an illuminating journey into the realm of derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions with our meticulously crafted worksheet. Dive deep into the intricacies of these essential mathematical tools, unlocking their power to unravel the mysteries of composite functions and real-world applications.
Within these pages, you’ll find a comprehensive exploration of inverse trigonometric derivatives, empowering you to navigate the complexities of calculus with newfound confidence.
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Derivatives Of Inverse Trig Functions Worksheet
Inverse trigonometric functions, also known as arcus functions, are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions. They play a crucial role in calculus, allowing us to find the derivatives of composite functions involving trigonometric functions.
Derivative Formulas
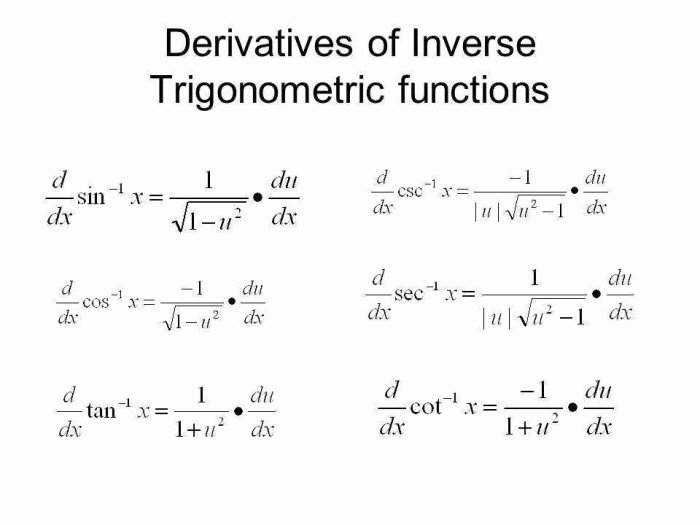
- arcsin(x) = 1/√(1-x²)
- arccos(x) = -1/√(1-x²)
- arctan(x) = 1/(1+x²)
- arccot(x) = -1/(1+x²)
- arcsec(x) = 1/|x|√(x²-1)
- arccsc(x) = -1/|x|√(x²-1)
These formulas are derived using the chain rule, which states that the derivative of a composite function is equal to the product of the derivatives of its constituent functions.
Applications in Calculus
Inverse trigonometric derivatives are used to find the derivatives of composite functions involving inverse trigonometric functions. For example, the derivative of y = arcsin(x²) is given by y’ = 2x/√(1-x⁴).
Inverse trigonometric derivatives have applications in various fields, including physics and engineering. For instance, they are used to analyze the motion of objects moving in circular or oscillatory motion.
Table of Derivatives, Derivatives of inverse trig functions worksheet
| Function | Derivative | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| arcsin(x) | 1/√(1-x²) | Used to find the derivative of y = arcsin(x). |
| arccos(x) | -1/√(1-x²) | Used to find the derivative of y = arccos(x). |
| arctan(x) | 1/(1+x²) | Used to find the derivative of y = arctan(x). |
| arccot(x) | -1/(1+x²) | Used to find the derivative of y = arccot(x). |
| arcsec(x) | 1/|x|√(x²-1) | Used to find the derivative of y = arcsec(x). |
| arccsc(x) | -1/|x|√(x²-1) | Used to find the derivative of y = arccsc(x). |
Worked Examples
- Find the derivative of y = arcsin(2x).
- Find the derivative of y = arctan(x²) + arccos(x).
- A particle moves in a circular motion with radius r. Its angular velocity is given by ω = arcsin(t/2). Find the particle’s tangential velocity at time t.
Practice Worksheet
- Find the derivative of y = arccos(x/2).
- Find the derivative of y = arctan(sin(x)).
- A projectile is launched with an initial velocity of v at an angle θ to the horizontal. Find the projectile’s horizontal velocity at time t.
Visual Representations
Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions and their derivatives can aid in understanding the concepts and memorizing the formulas. For example, the graph of y = arcsin(x) is a half-circle with radius 1. The derivative of y = arcsin(x), given by y’ = 1/√(1-x²), is the reciprocal of the cosine of the angle θ, where θ is the angle between the x-axis and the line connecting the point (x,y) to the origin.
FAQ
What is the significance of the chain rule in deriving inverse trigonometric derivatives?
The chain rule provides a systematic approach to differentiate composite functions, allowing us to break down complex functions into simpler components and apply the derivatives of individual functions.
How are inverse trigonometric derivatives used in real-world applications?
Inverse trigonometric derivatives find applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and computer graphics, where they are used to model periodic phenomena, solve differential equations, and perform transformations.