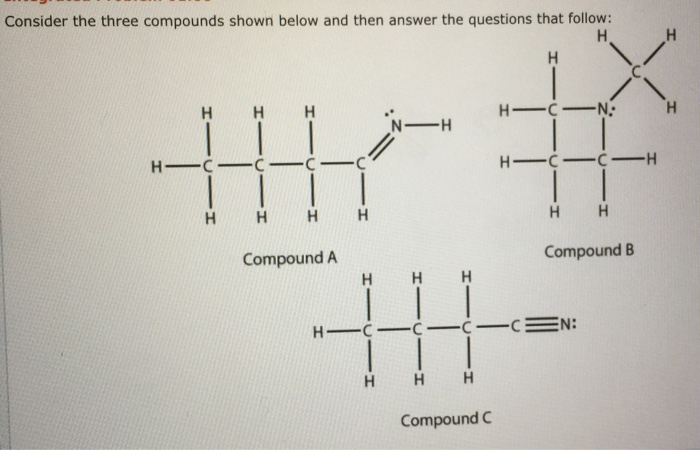
Consider these three compounds. which are isomers – Consider these three compounds: which are isomers sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Isomerism, a fundamental concept in chemistry, plays a pivotal role in shaping the properties and reactivity of molecules, and this captivating exploration delves into its intricacies, unraveling the secrets that lie within.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Isomerism Concepts
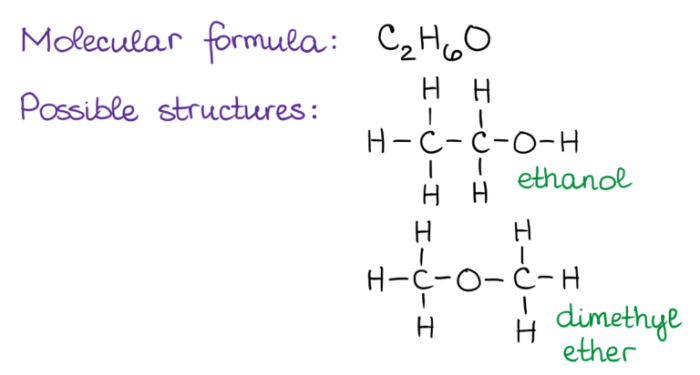
Isomerism is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the existence of compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in understanding the properties and reactivity of molecules.
Isomers can be classified into different types based on their structural differences:
- Structural isomershave the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule.
- Geometric isomershave the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms or groups around a double bond or a ring.
- Enantiomersare mirror-image isomers that are non-superimposable.
The molecular structure of a compound determines its isomerism. The presence of double bonds, rings, and chiral centers can give rise to different isomeric forms.
Identifying Isomers: Consider These Three Compounds. Which Are Isomers
Identifying isomers is crucial for understanding their properties and reactivity. Various techniques are employed to distinguish between isomers:
- Spectroscopy, such as NMR and IR spectroscopy, provides information about the molecular structure and functional groups present.
- Chromatography, including gas chromatography and liquid chromatography, separates isomers based on their different physical properties.
Chemical and physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility, can also be used to differentiate between isomers. Isomers can be separated and purified using techniques like fractional distillation, crystallization, and chromatography.
Isomer Properties and Reactivity
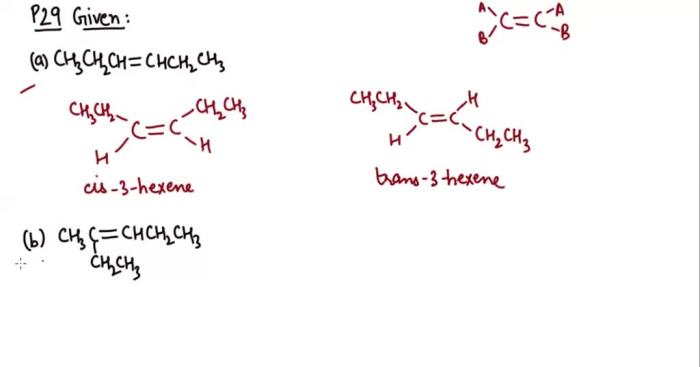
Isomers exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties due to their different molecular structures.
- Physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility, can vary significantly among isomers.
- Chemical properties, such as reactivity and selectivity, are also affected by isomerism. Isomers can react differently with other molecules due to their different spatial arrangements and electronic properties.
Isomerism plays a crucial role in drug design, where specific isomers may have different biological activities and side effects.
Isomerism in Biological Systems
Isomerism is a fundamental aspect of biological molecules, including DNA and proteins.
- DNAconsists of double-stranded helices with complementary base pairs that form isomers known as DNA isomers.
- Proteinsexhibit different isomeric forms due to the folding of polypeptide chains. Protein folding is influenced by isomerism and affects enzyme activity and protein function.
Understanding isomerism in biological systems is essential for comprehending biological processes and developing therapeutic strategies.
Question Bank
What is isomerism?
Isomerism is a phenomenon in which compounds with the same molecular formula have different structural arrangements, resulting in distinct properties.
How can isomers be identified?
Isomers can be identified using various techniques, including spectroscopy, chromatography, and analysis of their physical and chemical properties.
How does isomerism affect reactivity?
Isomerism can significantly influence the reactivity of compounds, as different isomers may exhibit varying reactivities due to differences in their molecular structures.