Reflection ratio for Earth’s atmosphere or service sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif and brimming with originality from the outset. This concept, pivotal in understanding Earth’s energy budget, forms the cornerstone of this exploration, unraveling its intricacies and highlighting its profound implications for our planet.
The reflection ratio, a measure of the fraction of solar radiation reflected back to space by Earth’s atmosphere, plays a critical role in regulating our planet’s temperature. By examining the factors that influence this ratio, such as wavelength, angle of incidence, and atmospheric composition, we gain insights into the complex interplay between Earth’s atmosphere and its energy balance.
Reflection Ratio Basics: Reflection Ratio For Earth’s Atmosphere Or Service
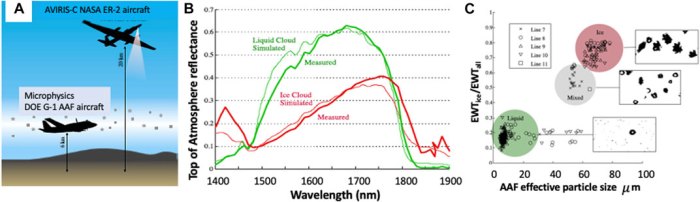
The reflection ratio is a measure of the amount of solar radiation that is reflected back to space by Earth’s atmosphere. It is an important factor in determining Earth’s energy budget and climate.
The reflection ratio is influenced by a number of factors, including the wavelength of the radiation, the angle of incidence, and the composition of the atmosphere.
Factors Influencing Reflection Ratio, Reflection ratio for earth’s atmosphere or service
- Wavelength:The reflection ratio is higher for shorter wavelengths (e.g., ultraviolet and visible light) than for longer wavelengths (e.g., infrared radiation).
- Angle of incidence:The reflection ratio is higher for radiation that strikes the atmosphere at a glancing angle than for radiation that strikes the atmosphere directly overhead.
- Atmospheric composition:The reflection ratio is affected by the presence of aerosols and clouds in the atmosphere. Aerosols and clouds can scatter and absorb solar radiation, reducing the amount of radiation that is reflected back to space.
| Wavelength (nm) | Reflection Ratio (%) | Atmospheric Condition |
|---|---|---|
| 250 | 5-10 | Clear sky |
| 500 | 20-30 | Clear sky |
| 1000 | 40-50 | Clear sky |
| 250 | 10-20 | Cloudy sky |
| 500 | 30-40 | Cloudy sky |
| 1000 | 50-60 | Cloudy sky |
Reflection Ratio and Earth’s Energy Budget

The reflection ratio plays a significant role in Earth’s energy budget. The amount of solar radiation that is absorbed by Earth is equal to the amount of radiation that is received from the Sun minus the amount of radiation that is reflected back to space.
A higher reflection ratio means that more solar radiation is reflected back to space, and less is absorbed by Earth. This can lead to a cooler Earth.
Conversely, a lower reflection ratio means that more solar radiation is absorbed by Earth, and less is reflected back to space. This can lead to a warmer Earth.

Measuring the Reflection Ratio

The reflection ratio of Earth’s atmosphere can be measured using a variety of methods, including:
- Satellite remote sensing:Satellites can be used to measure the amount of solar radiation that is reflected back to space at different wavelengths.
- Ground-based measurements:Ground-based instruments can be used to measure the amount of solar radiation that is reflected back to space at a single wavelength.
- Lidar:Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) can be used to measure the amount of aerosol and cloud cover in the atmosphere, which can affect the reflection ratio.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Satellite remote sensing provides global coverage, but it can be expensive and difficult to calibrate. Ground-based measurements are less expensive, but they only provide data for a single location.
Applications of Reflection Ratio
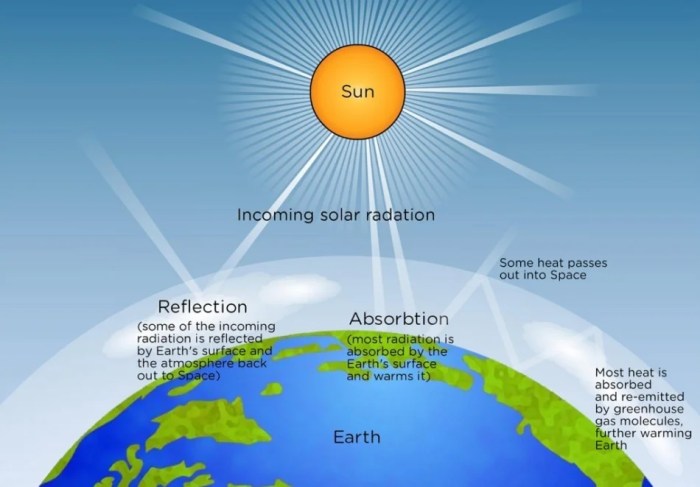
The reflection ratio is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Remote sensing:The reflection ratio can be used to map the distribution of aerosols and clouds in the atmosphere.
- Climate modeling:The reflection ratio is used in climate models to simulate the Earth’s energy budget and climate.
- Climate change research:The reflection ratio can be used to study how climate change is affecting the Earth’s energy budget and climate.
Future Research Directions
There are a number of areas where further research on reflection ratio is needed, including:
- Improved measurement techniques:New measurement techniques are needed to improve the accuracy and precision of reflection ratio measurements.
- Improved modeling approaches:Improved modeling approaches are needed to better simulate the reflection ratio and its effects on Earth’s energy budget and climate.
- Climate change impacts:More research is needed to understand how climate change is affecting the reflection ratio and its impacts on Earth’s energy budget and climate.
User Queries
What is the significance of the reflection ratio for Earth’s atmosphere?
The reflection ratio is crucial as it determines the amount of solar radiation absorbed by Earth, influencing its temperature and energy balance.
How is the reflection ratio measured?
Reflection ratio is measured using instruments such as satellites and ground-based radiometers, which detect the amount of solar radiation reflected back to space.
What are the applications of reflection ratio data?
Reflection ratio data is used in remote sensing, climate modeling, and understanding atmospheric processes, providing insights into Earth’s energy budget and climate change.